Understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of therapeutic products is an important step in their development as therapeutic entities. We offer a variety of rodent models and carry out pharmacodynamic (PD) and pharmacokinetic (PK) studies for your specific cell or biologics products.
Typically, the systemic concentration of TPs is determined in blood, plasma, or serum sampled from the relevant animal species, quantified using ligand-binding assays, such as ELISA, mass spectrometry assays, quantitative PCR (qPCR), or digital droplet PCR (ddPCR). For TPs with targets in non-systemic locations, it may be essential to characterize the biodistribution of the TP to the site of action and/or other tissues or fluids to aid translational PK/PD modeling or proof of mechanism of action. Biodistribution of TPs can be characterized by collecting tissue samples and measuring concentration of TP via bioanalytical methods, such as ELISA, mass spectrometry, immunohistochemistry, qPCR, or ddPCR. Alternatively, in vivo biodistribution may be measured in the intact animal via radiolabeling or fluorescence conjugation and then measured by positron emission tomography, immunofluorescence, or other imaging techniques. When multiple mechanisms are involved in the PK and biodistribution of a TP, in vivo biodistribution studies may only give an overall view of the net effect of the various processes. Thus, combining biodistribution data with additional in vitro analyses or within a mechanistic modeling framework could elucidate the relative contributions of each mechanism to the overall PK and biodistribution.
Examples of animal PK / PD Studies
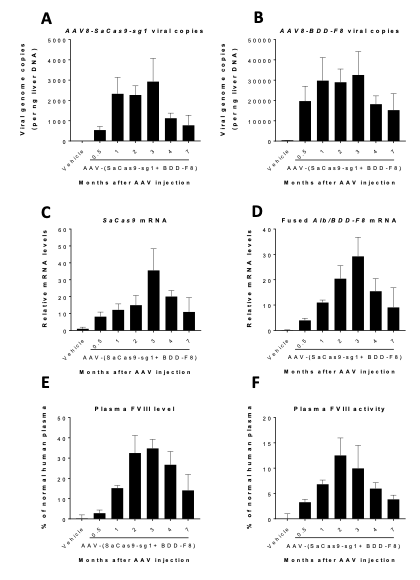
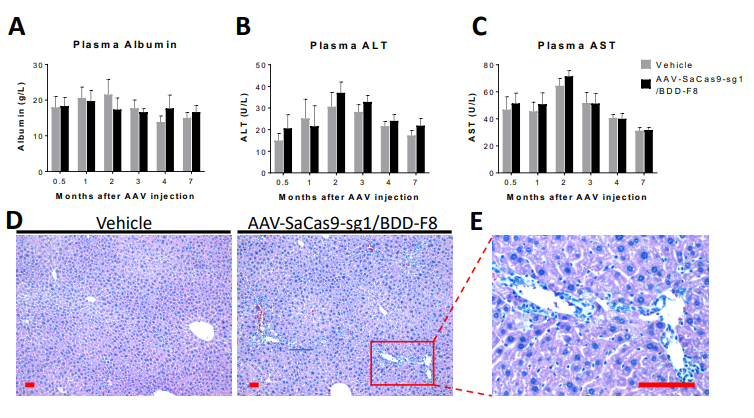
Clearance/Half-Life of AAV2/8-Mediated Gene Therapy of Human Factor VIII
Time course of targeted human BDD-F8 transgene expression and FVIII activity
From Applied StemCell’s publication: Scientific Reports 9(1) DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-53198-y
Dose Range and Function Study
AAV dose-dependent expression of the targeted human BDD-F8 transgene ameliorated hemophilia A in mice
Fill out the contact form below and a team member will be in touch within one business day.