A Class 2 Type V Cas12a nuclease, MAD7 is ideal for product development that relies on genome editing
While CRISPR/Cas9 revolutionized how we study biology, its intellectual property situation has always been complex. Depending on how you are using it, you might have to pay licensing fees to three different organizations.
Fortunately, in 2017, the team at Inscripta, Inc. generously gifted the scientific community with broad access to MAD7, to expand the impact of CRISPR-type technology.
MAD7, or ErCas12a, is a Class 2 Type V Cas nuclease from Eubacterium rectale. Like Cas9, MAD7 is an RNA-guided nuclease. However, unlike Cas9, MAD7:
We have years of success using MAD7 for gene editing in iPSC lines and HEK293 cells.
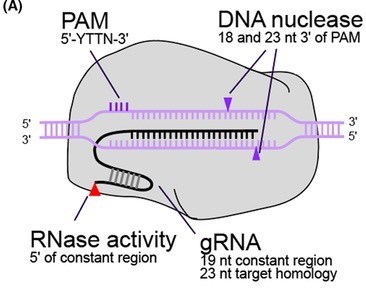
MAD7 can be used for many of the same applications as CRISPR/Cas9, including:
Cell line engineering
Product development
Fill out the contact form below and a team member will be in touch within one business day.