Discover Our iPSC Differentiated Cell Services
With the convenience of cell line models and the biorelevance of primary cells, iPSC-differentiated cell lines are an ideal, cutting-edge resource for disease modeling, drug discovery and screening, and regenerative medicine.
Applied StemCell (ASC) offers comprehensive customized service to differentiate iPSCs to many different progenitor and lineage-committed cell types (neural stem cells, cardiomyocytes, RPE, hematopoietic Progenitors, and more), thereby expanding the scope of your research, drug discovery, or drug screening projects.
Our custom iPSC differentiation service offers:
Our experts can differentiate your iPSCs or you can select from our inventory of well-characterized iPSC control lines. ASC even offers upstream iPSC generation from human or non-human samples and high-throughput CRISPR genome editing services. To learn more about our affordable, custom iPSC services contact us today.
We specialize in many different lineages: neural, hematopoietic, cardiovascular, photo receptors and more. See our not all-inclusive list of lineages we offer. Don’t see a lineage you are interested in? We also offer customized differentiation protocol development for lineages not listed.
PSC-derived, lineage committed cells offer a novel resource for drug discovery and drug screening processes that is gaining immense popularity. Considered as a more biorelevant with promising translational value, they offer a high-throughput model for toxicity and safety pharmacology assessments, disease modeling and proof of concept experiments, and for cell therapy applications. Neural lineage cells are especially advantageous for early, high-throughput neurotoxicity screening of compounds reducing attrition rate.
Need a CRO for screening your compounds for neuro / cardio toxicity and drug screening? Explore our preclinical services platform.
Neural Progenitor Cells (NPCs)
Case Study 1
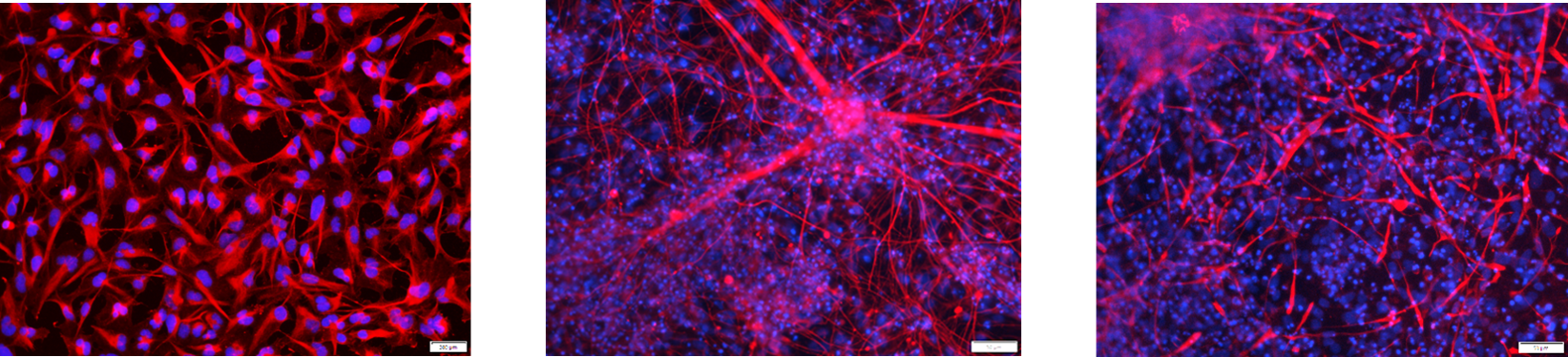
Figure 1. Immunostaining of the ASE-9740 Neural Progenitor Cells derived from Applied StemCell’s control iPSC line ASE-9211. The neural progenitor cells (NPCs) (Left, Red: Nestin; Blue: DAPI) can be further differentiated into neurons (Middle, Red: Tuj1; Blue: DAPI) and astrocytes (Right, Red: GFAP; Blue: DAPI).
Case Study 1
Project Description:
Timeline:
Turnaround time: 3-4 months
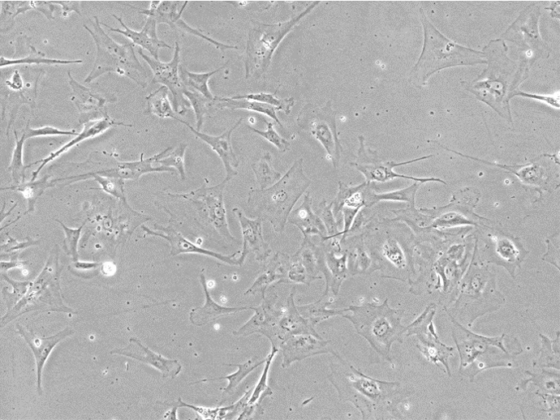
Figure 1. Bright Field Image of iPSC-derived Astrocytes from Applied StemCell’s (ASC’s) Control Line, ASE-9211.
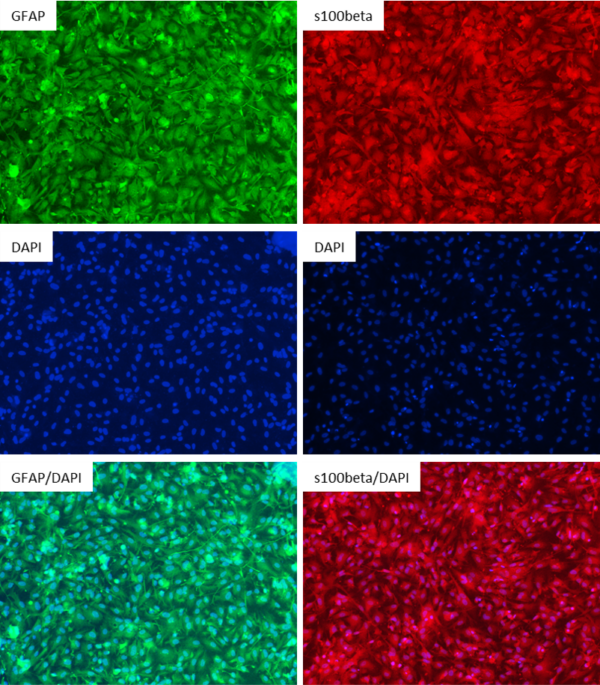
Figure 2: Antibody Staining of the Astrocytes differentiated from the NIST Control Line, ASE-9211. The astrocytes differentiated from the ASC’s iPSC line were stained with the astrocyte markers GFAP and s100beta. Left Three Images: Top Image: GFAP (Green), Middle Image: DAPI (Blue), Bottom Image: GFAP (Green) & DAPI (Blue); Right Three Images: Top Image: s100beta (Red), Middle Image: DAPI (Blue), Bottom Image: s100beta (Red) & DAPI (Blue)
Case Study 1
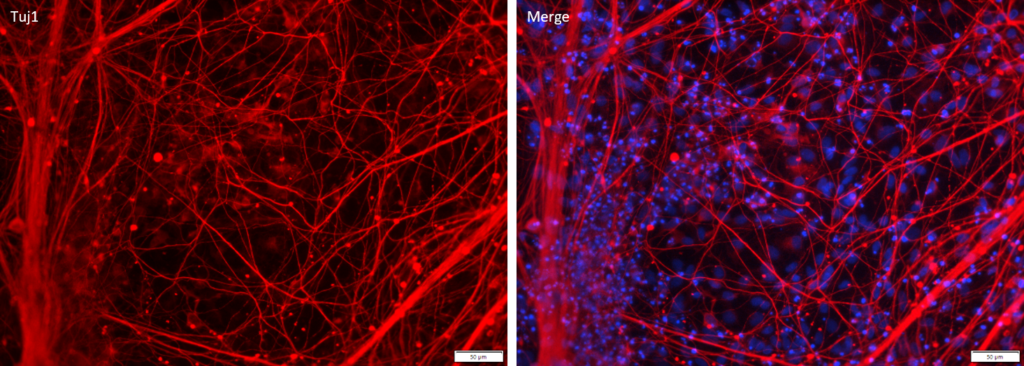
Figure 1. Immunostaining of ASE-9741 iPSC-derived Cortical Neurons for a cortical neuron biomarker. Cryopreserved cortical neurons, differentiated from Applied StemCell’s control iPSC line ASE-9211, were stained with Tuj1. (Red: Tuj1; Blue: DAPI)
Case Study 1
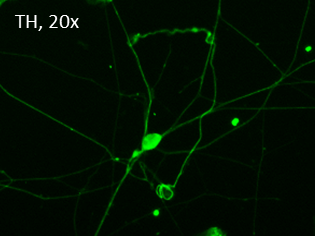
Figure 1. Immunostaining of the ASE-9742 Dopaminergic Neurons derived from the human iPSC control line ASE-9211. The progenitors were further differentiated into TH+ dopaminergic neurons in 3 weeks. The dopaminergic neurons were identified by TH.
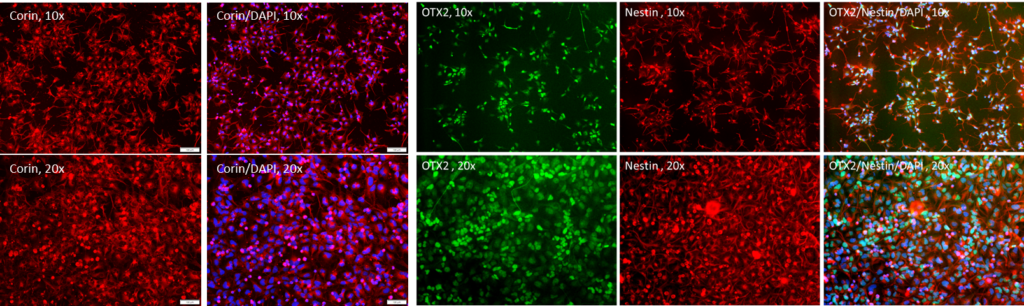
Figure 2. Immunostaining of the ASE-9742 Dopaminergic Progenitors. The dopaminergic progenitors were identified by Corin, OTX2, and Nestin.